| |
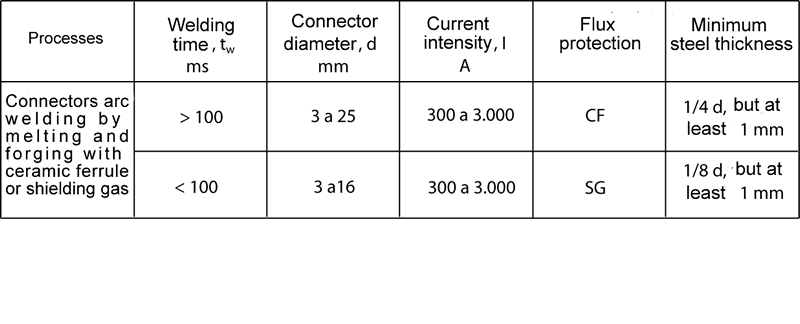
CERAMIC FERRULE
Ceramic ferrule, forming a combustion chamber around the welding, protects welder both from arc as projections. Concentrates the arc in a small area and limiting the heat losses and the cooling rate. The splint protects only slightly ambient air welding. When the connector is plunged into the weld pool, molten metal moves outward from the board to form an annular weld collar around the connector. The welding may thereby be performed at any position. The ceramic ferrule is used for a single welding and removed once the molten metal has solidified .
- The ceramic ferrule must be in contact with the metal base.
- The ceramic ferrule should be arranged concentrically with respect to the connector, and an inclination or an irregular contact between the ferrule and the connector leads to produce an irregular necklace and can prevent the collapse.
- The ceramic ferrules should be stored in a dry place.
- If the risk of hydrogen cracking, ceramic ferrules should be dried at high temperatures (1 h above 900 ° C).
GAS PROTECTION
Welding with shielding gas, the atmosphere around the arc is replaced by a shielding gas, which reduces the formation of blowholes. For steel and most metals, a mixture is used with a 82% argon and 18% carbon dioxide (EN 439-M21).
The shielding gas influences the arc and on the fusion of the connector and the workpiece tension modifying superficial melting bath, also influence on the shape of the weld collar and the shape of the penetration . As a fundamental principle, it should take the welding position PA according to EN ISO 6947. Can also be used to improve a ceramic ferrule collar shape and maintain the arc welding in an area close to the workpiece.
The gas is supplied by a device that should ensure a uniform gas shield, without turbulence.
Observe the following points:
- The arrival of gas should be annular (side of connector).
- The gas should displace the normal air temperature before starting the welding, it should be noted a preliminary period purge .
UNPROTECTED SHEAR CONNECTOR
Connector welding unprotected is only possible for small diameter (less than 10 mm) and short welding times (less than 100 ms). The disadvantages of this method are the high oxidation of the molten zone, an increase of the blowholes and an irregular seam.
A feature of the welding connectors is the very short duration of the arc time(between 0.5 ms and 3.0 ms) and accordingly the high heating and cooling rate .
METAL BASE
The arc of short duration causes the simultaneous fusion of the connector and the metal base , the two molten parts are mixed to form the modified solder changing the hea tproperties of the affected zone . This phenomenon varies according to diferent connector welding processes. In general, the volume of molten connector exceeds the volume of molten parent metal. Normally, the welding area on the metal base is larger than the cross section of the connector. The strength properties and deformation in the transition zone of the weld and the connector must be examined with special care.
- The surface of the metal base must be clean. Should be removed from the weld zone layers of paint, rust, scale, grease and non-weldable metal coatings. This can be accomplished by a mechanical or chemical process. Coated base metal oxid or scale are ground off perfectly.
- The Surfaces to be welded should be kept dry and free of condensation. When temperatures are below 5 ° C, appropriate preheating may be necessary.
- The quality of the welding of a shear connector depends not only on the strict adherence of the welding process specification, but also the proper operation of the drive mechanism, the state of the bonded, accessories and the supplied energy . |
|
|